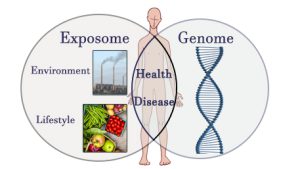
 A Recent review Assess the interaction between environmental exhibitions and human genome and show ways that this mutual disease can change the risk of the disease.
A Recent review Assess the interaction between environmental exhibitions and human genome and show ways that this mutual disease can change the risk of the disease.
Many diseases, such as congenital defects and developmental disability, type 2 diabetes and cancer, are affected by both environmental and genetic factors. The overall effects of environmental exhibitions are called pre -birth and the whole life exposed. Exhibition studies have identified the association between environmental exposure and disease, such as smoking and use of type 2 diabetes or alcohol and cystolic blood pressure. In addition to the exposure, genome also plays a role in the development and risk of disease. For some diseases such as cystic fibrosis, specific variations in the same gene can have the main influence on the development of the disease. For other diseases such as type 2 diabetes, the development of the disease can be affected by the small effects of many genes, but can still be greatly affected by environmental exposures, such as physical activity or diet.
Nor is the risk of disease or pathology in exposure or genome isolation. The interaction between these two sectors provides further information on the risk of developing diseases for individuals and populations. As a result, exposing the development of the disease and improving the prevention of diseases is an important step to understand the mutual interference between the genome and them.
Gene environmental interactions
One way to interact with exposes and genome is through the interaction of the gene environment. Genes refer to environmental conversations when the effects of environmental exposure vary among people with different gene types. For example, specific genetic shapes edit the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease after the exposure to organophosphate pesticides. Another scenario is that when people with the same geo -type, but people with different levels of environmental exposure can have different precision effects. For example, studies have seen either active and passive cigarette smoking exhibits for Delta F508 and have different effects on environmental exposure levels.
In addition to providing insights about biological mechanisms for diseases, the gene environmental interactions provide information, which can have a higher risk of the disease after environmental exposure.
Epagnitics
Another way to interact with the exposes genome is through epigentics, the process of changing the expression of the gene without changing the DNA continuity. Epigentics is a dynamic process that can be affected by genetic and environmental factors, such as smoking and air pollution. Although epigentic desserts is an important contribution to some diseases, such as Angelman Syndrome and some cancer, further investigations are needed to better understand how environmental changes in epilepsy affect the risk of the disease. Currently, epigentic markers can be used as bio -markers for environmental exposures, such as smoking and air pollution. Epilepsy has also been used as a marker for biological aging, which allows to allow how exposures can accelerate or reduce biological aging.
The implications of the health of the public
In addition to the risk of diseases and the amount of consequences, as well as a better understanding of interaction between genomics is essential to identify the population of worse results due to the amount of environmental exposure. More extensively, adding genomics to the health risk of environmental risk factors can strengthen the association’s useful interpretation between exposure and health results and can lead to precautionary intervention focused on amending risk factors.